What is Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market?
The Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market is a dynamic and evolving sector within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on the development and distribution of medications designed to manage and treat multiple sclerosis (MS). MS is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. The market for MS drugs is driven by the increasing prevalence of the disease, advancements in drug development, and a growing awareness of MS among healthcare professionals and patients. The market encompasses a variety of drug types, including injectable medications, oral medications, and other treatment forms, each offering different mechanisms of action and benefits. As the understanding of MS pathophysiology improves, pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative therapies that can better manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve the quality of life for patients. The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, regulatory challenges, and the need for continuous innovation to address unmet medical needs. Overall, the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market plays a crucial role in providing therapeutic solutions to individuals affected by this debilitating condition, with a focus on enhancing patient outcomes and advancing medical science.
Injectable Medications, Oral Medications, Others in the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market:
Injectable medications are a cornerstone in the treatment of multiple sclerosis, offering a reliable and effective means of managing the disease. These medications are typically administered through subcutaneous or intramuscular injections and work by modulating the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the nervous system. Common injectable drugs include interferon beta products and glatiramer acetate, which have been used for decades and are well-established in the treatment regimen for MS. Interferon beta drugs help to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, while glatiramer acetate is believed to mimic myelin protein, thereby diverting the immune response away from attacking the body's own nerve fibers. Despite their efficacy, injectable medications often come with challenges such as injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms, and the need for regular administration, which can affect patient adherence. However, advancements in formulation and delivery methods continue to improve the patient experience, making injectables a vital component of MS treatment. Oral medications, on the other hand, have gained popularity in recent years due to their convenience and ease of use. These drugs are taken in pill form and offer an alternative to injections, which can be particularly appealing to patients seeking a less invasive treatment option. Oral medications such as fingolimod, dimethyl fumarate, and teriflunomide work by targeting specific pathways involved in the immune response, thereby reducing inflammation and slowing disease progression. The introduction of oral therapies has revolutionized the MS treatment landscape, providing patients with more choices and flexibility in managing their condition. However, oral medications are not without their own set of challenges, including potential side effects such as liver toxicity, cardiovascular risks, and gastrointestinal issues. As a result, careful monitoring and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of these drugs. In addition to injectable and oral medications, the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market also includes other treatment options such as infusion therapies and emerging biologics. Infusion therapies, administered intravenously, offer targeted treatment for patients with more aggressive forms of MS or those who have not responded well to other therapies. These treatments, such as natalizumab and ocrelizumab, work by blocking specific immune cells from crossing the blood-brain barrier, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing further damage to the nervous system. While infusion therapies can be highly effective, they require administration in a clinical setting and carry risks such as infusion reactions and increased susceptibility to infections. Emerging biologics represent a promising frontier in MS treatment, with ongoing research focused on developing novel therapies that target specific pathways involved in the disease process. These innovative treatments aim to provide more personalized and effective options for patients, addressing the diverse needs of the MS population. Overall, the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market offers a wide range of treatment options, each with its own benefits and challenges, underscoring the importance of personalized care and informed decision-making in managing this complex disease.
Adults, Children in the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market:
The usage of Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market extends across different age groups, with specific considerations for adults and children affected by the disease. In adults, multiple sclerosis is more commonly diagnosed, and the treatment approach is often tailored to the individual's specific symptoms, disease progression, and lifestyle needs. Adult patients have access to a wide range of therapeutic options, including injectable medications, oral drugs, and infusion therapies, each offering different mechanisms of action and benefits. The choice of treatment is influenced by factors such as the severity of the disease, the patient's overall health, and their preferences regarding administration methods. For many adults, managing MS involves a combination of pharmacological treatments, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies to address symptoms such as fatigue, mobility issues, and cognitive changes. Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential to assess treatment efficacy, manage side effects, and make necessary adjustments to the therapeutic regimen. In children, multiple sclerosis is relatively rare, but when it occurs, it presents unique challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment. Pediatric MS requires a specialized approach, as children may experience different symptoms and disease progression compared to adults. The treatment of pediatric MS often involves a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including neurologists, pediatricians, and rehabilitation specialists, to provide comprehensive care. Injectable medications, such as interferon beta and glatiramer acetate, are commonly used in children, although the dosing and administration may be adjusted to accommodate their smaller size and developing bodies. Oral medications may also be considered, but careful monitoring is crucial to ensure safety and efficacy in this population. In addition to pharmacological treatments, children with MS benefit from supportive therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and counseling to address the physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges associated with the disease. Education and support for families are also vital components of pediatric MS care, helping parents and caregivers navigate the complexities of the disease and advocate for their child's needs. Overall, the usage of Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market in adults and children highlights the importance of personalized care and a holistic approach to treatment, recognizing the diverse needs and challenges faced by individuals across different age groups.
Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market Outlook:
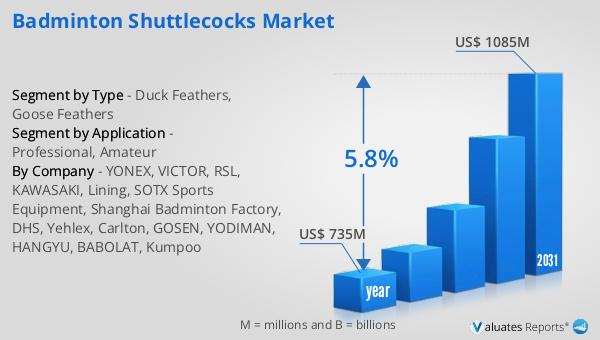
The worldwide market for Multiple Sclerosis Drugs was valued at $16,560 million in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to a revised size of $23,200 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.0% during the forecast period. In the broader context, the global pharmaceutical market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with an expected growth rate of 5% over the next six years. Comparatively, the chemical drug market is projected to grow from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion by 2022. This data underscores the significant role that the Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market plays within the larger pharmaceutical industry, highlighting its steady growth and the increasing demand for effective MS treatments. The market's expansion is driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of multiple sclerosis, advancements in drug development, and a growing awareness of the disease among healthcare professionals and patients. As pharmaceutical companies continue to invest in research and development, the introduction of innovative therapies is expected to further propel market growth, offering new hope and improved outcomes for individuals living with MS. The competitive landscape of the market is characterized by the presence of key players, regulatory challenges, and the need for continuous innovation to address unmet medical needs. Overall, the Global Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market is poised for continued growth, playing a crucial role in providing therapeutic solutions to individuals affected by this debilitating condition and advancing medical science.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Multiple Sclerosis Drugs Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 16560 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 23200 million |
| CAGR | 5.0% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type | |
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Biogen, Sanofi, Novartis, Teva, Merck KGaA, Bayer, ACORDA, Mallinckrodt |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |