What is Global Glutamic Acid Market?
The Global Glutamic Acid Market refers to the worldwide industry focused on the production, distribution, and consumption of glutamic acid, a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. Glutamic acid is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, particularly in the form of monosodium glutamate (MSG), which is popular for its ability to enhance the umami taste in foods. Beyond its culinary applications, glutamic acid is also significant in the pharmaceutical industry, where it is used in the formulation of medications and supplements due to its role in neurotransmission and brain health. Additionally, it is utilized in animal and pet food to improve palatability and nutritional value. The market for glutamic acid is driven by its diverse applications and the growing demand for processed and convenience foods, as well as the increasing awareness of its health benefits. As a result, the global glutamic acid market is experiencing steady growth, with manufacturers and suppliers focusing on expanding their production capacities and exploring new applications to meet the rising demand. The market is characterized by a mix of established players and new entrants, all striving to innovate and capture a larger share of this dynamic industry.
Biosynthesis, Industrial Synthesis in the Global Glutamic Acid Market:
Biosynthesis and industrial synthesis are two primary methods for producing glutamic acid, each with its own set of processes and applications within the global glutamic acid market. Biosynthesis refers to the natural production of glutamic acid within living organisms. In plants, animals, and microorganisms, glutamic acid is synthesized through metabolic pathways involving the conversion of other amino acids or intermediates. In plants, for example, glutamic acid is produced via the reductive amination of α-ketoglutarate, a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, using the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase. This process is crucial for nitrogen assimilation and amino acid metabolism in plants. In animals, glutamic acid is synthesized from α-ketoglutarate and ammonia through a similar enzymatic reaction, playing a vital role in protein synthesis and neurotransmitter regulation. Microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, also produce glutamic acid through fermentation processes, which are harnessed in industrial applications to produce glutamic acid on a large scale. Industrial synthesis of glutamic acid primarily involves microbial fermentation, a process that has been optimized over the years to enhance yield and efficiency. This method typically employs strains of Corynebacterium glutamicum or Escherichia coli, which are genetically engineered to overproduce glutamic acid. The fermentation process involves cultivating these microorganisms in a nutrient-rich medium containing carbon sources such as glucose or molasses, nitrogen sources, and other essential nutrients. Under controlled conditions, the microorganisms convert the substrates into glutamic acid, which is then extracted and purified for various applications. The industrial synthesis of glutamic acid is a cost-effective and sustainable method, as it utilizes renewable resources and produces minimal waste. Advances in biotechnology and genetic engineering have further improved the efficiency of microbial fermentation, enabling higher yields and reduced production costs. This has contributed to the widespread availability and affordability of glutamic acid in the global market. In addition to microbial fermentation, chemical synthesis methods have also been explored for glutamic acid production. These methods involve the chemical conversion of precursor compounds into glutamic acid through a series of reactions. However, chemical synthesis is less commonly used due to its higher cost and environmental impact compared to microbial fermentation. The choice between biosynthesis and industrial synthesis depends on factors such as cost, scalability, and environmental considerations. While biosynthesis is a natural and sustainable method, industrial synthesis offers the advantage of large-scale production and consistency in quality. As the demand for glutamic acid continues to grow, manufacturers are investing in research and development to optimize production processes and explore new technologies for sustainable and efficient synthesis. Overall, the global glutamic acid market is driven by the interplay of biosynthesis and industrial synthesis, with each method contributing to the availability and diversity of glutamic acid products in various industries.
Pharmaceutical, Food Additives, Animal & Pet Food in the Global Glutamic Acid Market:
The global glutamic acid market finds extensive applications across several industries, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, and animal and pet food, each leveraging the unique properties of glutamic acid to enhance their products. In the pharmaceutical industry, glutamic acid is valued for its role in neurotransmission and brain health. It is a precursor to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is crucial for regulating nerve impulses in the brain. As such, glutamic acid is used in the formulation of medications and dietary supplements aimed at improving cognitive function, treating neurological disorders, and supporting mental health. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it an effective component in therapies targeting brain-related conditions. Additionally, glutamic acid is used in the production of certain antibiotics and as a stabilizer in pharmaceutical formulations, enhancing the efficacy and shelf-life of medications. In the food industry, glutamic acid is primarily used as a flavor enhancer in the form of monosodium glutamate (MSG). MSG is widely recognized for its ability to enhance the umami taste, a savory flavor that is one of the five basic tastes alongside sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. The addition of MSG to food products enhances their palatability and flavor profile, making them more appealing to consumers. It is commonly used in processed foods, snacks, soups, sauces, and seasonings, contributing to the overall taste experience. Despite some controversy surrounding its use, MSG is considered safe for consumption by regulatory authorities worldwide, and its popularity continues to drive demand in the food additives market. In the animal and pet food industry, glutamic acid is used to improve the palatability and nutritional value of feed products. Animals, like humans, have taste receptors that respond to umami flavors, making glutamic acid an effective additive for enhancing the taste of animal feed. This is particularly important in pet food, where flavor and aroma play a significant role in consumer preferences. By incorporating glutamic acid into pet food formulations, manufacturers can create products that are more appealing to pets, encouraging better feed intake and overall nutrition. Additionally, glutamic acid serves as a source of nitrogen and amino acids, contributing to the nutritional balance of animal diets. The use of glutamic acid in these industries highlights its versatility and importance as a functional ingredient. Its ability to enhance flavor, support brain health, and improve nutritional profiles makes it a valuable component in a wide range of products. As consumer demand for high-quality, flavorful, and nutritious products continues to grow, the global glutamic acid market is poised for sustained growth, driven by its diverse applications and the ongoing innovation in product development.
Global Glutamic Acid Market Outlook:
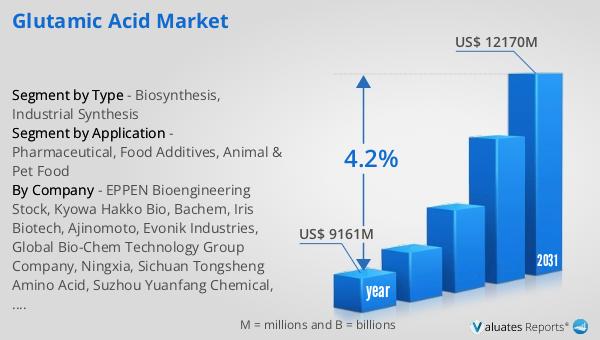
In 2024, the global market for glutamic acid was valued at approximately $9,161 million. Looking ahead, this market is expected to expand significantly, reaching an estimated size of $12,170 million by the year 2031. This growth trajectory represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% over the forecast period. This steady increase in market value underscores the rising demand for glutamic acid across various industries, driven by its versatile applications and the growing consumer awareness of its benefits. The expansion of the market can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing consumption of processed and convenience foods, where glutamic acid is used as a flavor enhancer. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry's demand for glutamic acid in the formulation of medications and supplements is contributing to market growth. The animal and pet food sectors are also playing a role, as glutamic acid is used to improve the palatability and nutritional value of feed products. As manufacturers continue to innovate and explore new applications for glutamic acid, the market is expected to maintain its upward trajectory, offering opportunities for growth and development in the coming years.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Glutamic Acid Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 9161 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 12170 million |
| CAGR | 4.2% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type | |
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | EPPEN Bioengineering Stock, Kyowa Hakko Bio, Bachem, Iris Biotech, Ajinomoto, Evonik Industries, Global Bio-Chem Technology Group Company, Ningxia, Sichuan Tongsheng Amino Acid, Suzhou Yuanfang Chemical, Akzo Nobel |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
