What is Global Anticoagulants Drug Market?
The Global Anticoagulants Drug Market is a significant segment within the pharmaceutical industry, focusing on medications that help prevent blood clots, which can lead to serious conditions like strokes, heart attacks, and deep vein thrombosis. These drugs are crucial for patients with various cardiovascular diseases, atrial fibrillation, and those who have undergone surgeries that increase the risk of clot formation. The market is driven by the rising prevalence of these conditions, an aging population, and the increasing awareness of the benefits of anticoagulant therapy. Technological advancements and the development of novel drugs have also contributed to the market's growth. The demand for anticoagulants is expected to continue rising as healthcare systems worldwide focus on preventive care and managing chronic conditions. This market is characterized by a mix of well-established drugs and newer entrants, offering a range of options for patients and healthcare providers. The competition among pharmaceutical companies to innovate and improve the efficacy and safety of these drugs is intense, leading to continuous research and development efforts. Overall, the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market plays a vital role in modern healthcare, providing essential treatments that improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs), Warfarin (VKA), Others in the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market:
Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs), Warfarin (VKA), and other anticoagulants are key components of the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market, each with unique characteristics and applications. NOACs, including drugs like rivaroxaban, apixaban, and dabigatran, have gained popularity due to their ease of use and fewer dietary restrictions compared to traditional anticoagulants like warfarin. NOACs work by directly inhibiting specific clotting factors, offering a more predictable anticoagulation effect, which reduces the need for regular blood monitoring. This convenience has made NOACs a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers, especially for those with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism. However, NOACs are generally more expensive than warfarin, which can be a consideration for some healthcare systems and patients. Warfarin, a Vitamin K antagonist (VKA), has been a staple in anticoagulation therapy for decades. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, effectively reducing the blood's ability to clot. Despite its effectiveness, warfarin requires regular blood tests to monitor its anticoagulation effect and has numerous dietary and drug interactions, which can complicate its use. Nevertheless, warfarin remains widely used, particularly in settings where cost is a significant factor, and in patients with mechanical heart valves, where NOACs are not recommended. Other anticoagulants in the market include heparin and low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs), which are often used in hospital settings for acute anticoagulation needs. Heparin is administered intravenously or subcutaneously and is commonly used in surgical and critical care settings due to its rapid onset of action. LMWHs, such as enoxaparin, offer the advantage of subcutaneous administration with a more predictable anticoagulation effect, making them suitable for outpatient use as well. These drugs are particularly useful in the prevention and treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The choice between NOACs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants depends on various factors, including the patient's medical condition, risk of bleeding, cost considerations, and the need for regular monitoring. Healthcare providers must weigh these factors to determine the most appropriate anticoagulation therapy for each patient. As the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve the safety, efficacy, and accessibility of these vital medications, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Hospital, Clinic, Others in the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market:
The usage of anticoagulants in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings is a critical aspect of the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market. In hospitals, anticoagulants are commonly used for both prophylactic and therapeutic purposes. Patients undergoing major surgeries, such as orthopedic or cardiac procedures, are often at increased risk of developing blood clots. In these cases, anticoagulants are administered to prevent postoperative complications like deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Additionally, patients admitted with acute medical conditions, such as heart attacks or strokes, may receive anticoagulants as part of their treatment regimen to prevent further clot formation and improve outcomes. The hospital setting also allows for close monitoring of patients receiving anticoagulants, ensuring that any potential side effects or complications are promptly addressed. In clinics, anticoagulants are primarily used for the long-term management of chronic conditions that increase the risk of clotting. Patients with atrial fibrillation, for example, are often prescribed anticoagulants to reduce their risk of stroke. Clinics provide an environment where patients can receive regular follow-up care, including blood tests for those on warfarin, to ensure that their anticoagulation therapy is effective and safe. The convenience of NOACs, which require less frequent monitoring, has made them a popular choice in outpatient settings, allowing patients to maintain their treatment regimen with minimal disruption to their daily lives. Other healthcare settings, such as nursing homes and home healthcare services, also play a role in the administration of anticoagulants. In these environments, anticoagulants are used to manage the risk of clotting in elderly or immobile patients, who may be at higher risk due to their age or limited mobility. The use of anticoagulants in these settings requires careful coordination between healthcare providers, caregivers, and patients to ensure adherence to treatment plans and monitoring for potential side effects. Overall, the use of anticoagulants across various healthcare settings highlights the importance of these drugs in preventing and managing conditions associated with blood clots. As the Global Anticoagulants Drug Market continues to grow, the focus remains on improving patient outcomes through effective and safe anticoagulation therapy, tailored to the needs of each individual patient.
Global Anticoagulants Drug Market Outlook:
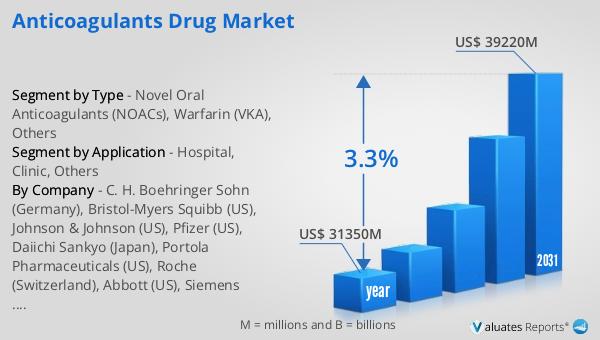
The global market for anticoagulant drugs was valued at approximately $31,350 million in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to around $39,220 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.3% over the forecast period. In the broader context of the pharmaceutical industry, the global market was valued at $1,475 billion in 2022, with an expected growth rate of 5% over the next six years. Comparatively, the chemical drug market is projected to grow from $1,005 billion in 2018 to $1,094 billion by 2022. This data underscores the significant role that anticoagulants play within the pharmaceutical sector, driven by the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and the growing demand for effective blood-thinning medications. The steady growth of the anticoagulants market is indicative of the ongoing need for these critical medications, as healthcare systems worldwide continue to prioritize the management and prevention of conditions associated with blood clots. The competition among pharmaceutical companies to innovate and improve the efficacy and safety of anticoagulants is expected to drive further advancements in this field, ensuring that patients have access to the most effective treatments available.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Anticoagulants Drug Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 31350 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 39220 million |
| CAGR | 3.3% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | C. H. Boehringer Sohn (Germany), Bristol-Myers Squibb (US), Johnson & Johnson (US), Pfizer (US), Daiichi Sankyo (Japan), Portola Pharmaceuticals (US), Roche (Switzerland), Abbott (US), Siemens (Germany), Alere (US), CoaguSense (US) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
