What is Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market?
The Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market is a specialized segment within the broader textile industry, focusing on fibers that have a lower melting point compared to traditional fibers. These fibers are engineered to melt at lower temperatures, typically below 130°C, which allows them to bond with other fibers without the need for additional adhesives. This unique property makes them highly valuable in various applications, including automotive, home textiles, and construction. The market for these fibers is driven by their versatility and the growing demand for sustainable and efficient materials. As industries continue to seek out eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions, low melting staple fibers offer an attractive option due to their ability to enhance product performance while reducing environmental impact. The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, each tailored to meet specific industry needs, and is supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving fiber properties and expanding their application scope. As a result, the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing awareness of the benefits these fibers offer across various sectors.
Melting Point ≤130 ℃, Melting Point >130 ℃ in the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market:
In the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market, fibers are categorized based on their melting points, specifically those with a melting point of ≤130°C and those with a melting point >130°C. Fibers with a melting point of ≤130°C are particularly advantageous in applications where low-temperature bonding is required. These fibers can be used in processes that involve heat-sensitive materials, ensuring that the integrity of the materials is maintained while achieving strong bonding. This category of fibers is often utilized in the production of nonwoven fabrics, which are used in a variety of applications such as hygiene products, filtration, and insulation. The ability to bond at lower temperatures not only reduces energy consumption but also minimizes the risk of damaging other materials during the manufacturing process. On the other hand, fibers with a melting point >130°C are designed for applications that require higher thermal resistance. These fibers are suitable for environments where higher temperatures are encountered, providing durability and stability under such conditions. They are often used in automotive interiors, where they contribute to the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of components. The higher melting point ensures that the fibers maintain their properties even when exposed to elevated temperatures, making them ideal for use in challenging environments. Both categories of fibers are integral to the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market, offering solutions that cater to a wide range of industrial needs. The choice between fibers with different melting points depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as temperature exposure, bonding strength, and material compatibility. As industries continue to innovate and seek out materials that offer both performance and sustainability, the demand for low melting staple fibers with varying melting points is expected to grow. This growth is supported by advancements in fiber technology, which are enabling the development of fibers with enhanced properties and broader application potential. The Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market is thus characterized by a dynamic interplay between technological innovation and market demand, driving the evolution of fiber products that meet the diverse needs of modern industries.
Automotive, Home Textile, Construction, Others in the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market:
The Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market finds extensive usage across various sectors, including automotive, home textiles, construction, and others. In the automotive industry, these fibers are used to enhance the performance and durability of interior components. They provide a lightweight and cost-effective solution for bonding materials, contributing to the overall efficiency and sustainability of vehicles. The ability to bond at lower temperatures also reduces energy consumption during manufacturing, aligning with the industry's push towards greener production methods. In home textiles, low melting staple fibers are used to create products that are both comfortable and durable. They are often used in the production of bedding, upholstery, and carpets, where they provide a soft feel while ensuring long-lasting performance. The fibers' ability to bond with other materials without the need for additional adhesives makes them an attractive option for manufacturers looking to streamline production processes and reduce costs. In the construction industry, these fibers are used to reinforce materials and improve the thermal and acoustic insulation properties of buildings. They are often incorporated into nonwoven fabrics used in roofing, wall coverings, and flooring, where they contribute to the structural integrity and energy efficiency of buildings. The versatility of low melting staple fibers also extends to other sectors, where they are used in applications ranging from filtration to packaging. The fibers' unique properties make them suitable for a wide range of uses, providing manufacturers with the flexibility to develop innovative products that meet the evolving needs of consumers. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, the demand for low melting staple fibers is expected to increase, driving further growth in the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market.
Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market Outlook:
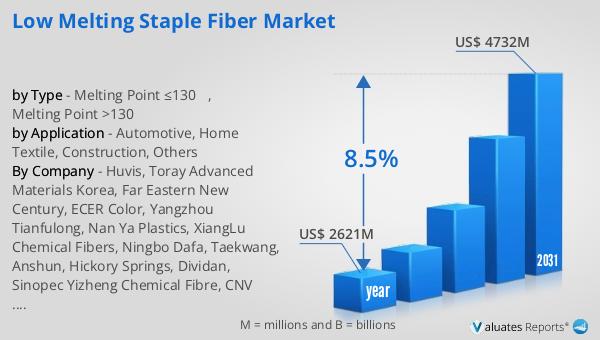
The global market for Low Melting Staple Fiber was valued at $2,621 million in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to a revised size of $4,732 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% during the forecast period. This growth trajectory underscores the increasing demand for these fibers across various industries, driven by their unique properties and the growing emphasis on sustainable materials. The market's expansion is indicative of the broader trend towards eco-friendly and efficient solutions, as industries seek to reduce their environmental footprint while enhancing product performance. The projected growth rate highlights the significant opportunities within the market, as advancements in fiber technology continue to unlock new applications and improve the performance of existing products. As the market evolves, companies are likely to invest in research and development to further enhance the properties of low melting staple fibers, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly demanding marketplace. The anticipated growth in the Global Low Melting Staple Fiber Market reflects the broader shift towards sustainable and innovative materials, positioning these fibers as a key component in the future of various industries.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Low Melting Staple Fiber Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 2621 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 4732 million |
| CAGR | 8.5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Huvis, Toray Advanced Materials Korea, Far Eastern New Century, ECER Color, Yangzhou Tianfulong, Nan Ya Plastics, XiangLu Chemical Fibers, Ningbo Dafa, Taekwang, Anshun, Hickory Springs, Dividan, Sinopec Yizheng Chemical Fibre, CNV Corporation, Shyam Fibers |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |