What is Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market?
The Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market is a specialized segment within the broader fiber industry, focusing on fibers that have a lower melting point compared to traditional fibers. These fibers are engineered to melt at lower temperatures, making them ideal for applications where bonding and thermal fusion are required without compromising the structural integrity of the materials involved. The market for these fibers is driven by their versatility and the growing demand across various industries such as automotive, textiles, and construction. These fibers are often used as a bonding agent in nonwoven fabrics, enhancing the durability and performance of the final product. The ability to melt and bond at lower temperatures not only saves energy but also reduces the risk of damaging sensitive materials during processing. As industries continue to seek more efficient and sustainable materials, the demand for low melting point composite fibers is expected to grow, offering innovative solutions for modern manufacturing challenges. The market is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the properties and applications of these fibers, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of different sectors.
Melting Point≤130 ℃, Melting Point>130 ℃ in the Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market:
In the Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market, fibers are categorized based on their melting points, specifically those with melting points ≤130 ℃ and those with melting points >130 ℃. Fibers with a melting point ≤130 ℃ are particularly valuable in applications where low-temperature processing is crucial. These fibers are often used in the textile industry for creating nonwoven fabrics, where they act as a bonding agent, providing strength and durability without the need for high-temperature processing. This is especially beneficial in applications where heat-sensitive materials are involved, as it minimizes the risk of damage. On the other hand, fibers with a melting point >130 ℃ are used in applications that require slightly higher processing temperatures. These fibers offer a balance between thermal resistance and bonding capability, making them suitable for more demanding applications where a higher degree of thermal stability is required. Both categories of fibers are integral to the market, offering solutions that cater to a wide range of industrial needs. The choice between these fibers depends largely on the specific requirements of the application, including the materials involved, the desired properties of the final product, and the processing conditions. As industries continue to innovate and seek more efficient materials, the demand for both types of low melting point composite fibers is expected to grow, driven by their ability to enhance product performance while reducing energy consumption and processing costs. The market is also influenced by advancements in fiber technology, which are continually expanding the range of applications for these materials. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve the properties of these fibers, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of various industries. This ongoing innovation is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the market and addressing the challenges posed by changing consumer demands and environmental considerations.
Automobile Industry, Textile Industry, Achitechive, Other in the Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market:
The Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market finds extensive usage across several industries, each leveraging the unique properties of these fibers to enhance their products and processes. In the automobile industry, these fibers are used in the production of interior components such as seat covers, carpets, and insulation materials. Their ability to bond at lower temperatures makes them ideal for creating lightweight, durable components that contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles. The textile industry also benefits significantly from these fibers, particularly in the production of nonwoven fabrics. These fabrics are used in a variety of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial materials, where the fibers provide strength and durability without the need for high-temperature processing. In the field of architecture, low melting point composite fibers are used in the production of construction materials such as insulation panels and roofing materials. Their thermal bonding properties enhance the structural integrity and energy efficiency of buildings, making them a valuable component in sustainable construction practices. Additionally, these fibers are used in other industries, including packaging and filtration, where their unique properties offer solutions for improving product performance and reducing environmental impact. The versatility and efficiency of low melting point composite fibers make them an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to enhance their products and processes while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact. As industries continue to evolve and prioritize sustainability, the demand for these fibers is expected to grow, driven by their ability to meet the diverse needs of modern manufacturing.
Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market Outlook:
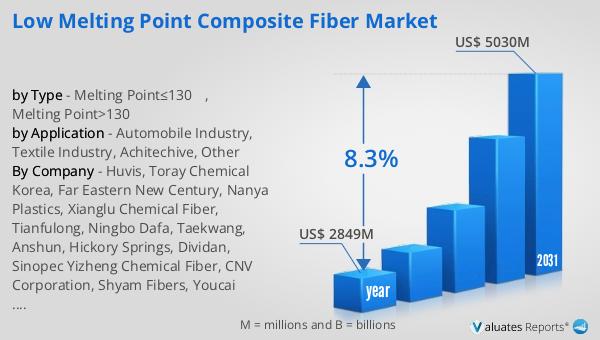
The global market for Low Melting Point Composite Fiber was valued at $2,849 million in 2024 and is anticipated to expand to a revised size of $5,030 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% during the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the increasing demand for these fibers across various industries, driven by their unique properties and the need for more efficient and sustainable materials. At present, Huvis stands as a global leader in this market, holding a 20% market share in 2024. This leadership position underscores the company's commitment to innovation and quality, as well as its ability to meet the evolving needs of its customers. The market's growth is supported by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the properties and applications of low melting point composite fibers, ensuring they remain relevant in a rapidly changing industrial landscape. As more industries recognize the benefits of these fibers, including their energy efficiency and versatility, the market is poised for continued expansion, offering new opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers alike. The future of the Global Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market looks promising, with advancements in technology and increasing awareness of sustainability driving demand for these innovative materials.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Low Melting Point Composite Fiber Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 2849 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 5030 million |
| CAGR | 8.3% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Huvis, Toray Chemical Korea, Far Eastern New Century, Nanya Plastics, Xianglu Chemical Fiber, Tianfulong, Ningbo Dafa, Taekwang, Anshun, Hickory Springs, Dividan, Sinopec Yizheng Chemical Fiber, CNV Corporation, Shyam Fibers, Youcai Environmental Resources Technology |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |