What is Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market?
The Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market is a specialized segment within the broader polyester fiber industry. This market focuses on fibers that have a lower melting point compared to standard polyester fibers, making them particularly useful in applications where bonding and thermal properties are crucial. These fibers are primarily used in the production of nonwoven fabrics, which are essential in various industries such as automotive, textiles, and construction. The unique properties of low melt polyester staple fibers, such as their ability to bond with other fibers at lower temperatures, make them highly sought after for applications that require durability and flexibility. The market is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials, especially in emerging economies where industrialization and urbanization are on the rise. As industries continue to seek materials that offer both performance and cost-effectiveness, the global low melt polyester staple fiber market is expected to grow steadily, driven by innovations and advancements in fiber technology.
in the Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market:
The Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market offers a variety of types that cater to the diverse needs of its customers. These fibers are primarily categorized based on their denier, which is a unit of measurement that describes the fiber's thickness. Customers in different industries select fibers with specific deniers to meet their unique requirements. For instance, in the textile industry, finer denier fibers are often preferred for creating soft and delicate fabrics, while coarser denier fibers are used for more robust applications such as upholstery and industrial textiles. Additionally, these fibers can be differentiated based on their cross-sectional shapes, which can influence the texture and performance of the final product. Some common shapes include round, trilobal, and hollow, each offering distinct advantages. Round fibers are typically used for general applications due to their balanced properties, while trilobal fibers are favored for their enhanced luster and bulkiness, making them ideal for carpets and decorative textiles. Hollow fibers, on the other hand, provide excellent insulation and are often used in applications where thermal properties are crucial, such as in bedding and outerwear. Furthermore, low melt polyester staple fibers are available in various colors and finishes, allowing manufacturers to create products that meet specific aesthetic and functional requirements. This versatility makes them a popular choice across multiple sectors, including automotive, construction, and home furnishings. In the automotive industry, for example, these fibers are used in the production of interior components such as seat covers and headliners, where their ability to bond with other materials enhances durability and comfort. In construction, they are used in geotextiles and insulation materials, providing strength and thermal efficiency. The adaptability of low melt polyester staple fibers to different processing techniques, such as needle punching and thermal bonding, further expands their application range. Needle punching is a mechanical process that interlocks fibers to create a nonwoven fabric, while thermal bonding uses heat to fuse fibers together, resulting in a strong and cohesive material. These processes allow manufacturers to produce a wide array of products that meet the specific demands of their customers. As the market continues to evolve, the development of new fiber types and processing technologies will likely lead to even more innovative applications, further solidifying the importance of low melt polyester staple fibers in various industries.
Automobile, Textile, Architecture, Others in the Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market:
The usage of Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market spans several key areas, including the automobile, textile, architecture, and other sectors. In the automobile industry, these fibers are integral to the production of interior components such as seat covers, headliners, and door panels. Their ability to bond with other materials at lower temperatures enhances the durability and comfort of these components, making them ideal for use in vehicles. Additionally, the lightweight nature of these fibers contributes to the overall reduction in vehicle weight, which can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. In the textile industry, low melt polyester staple fibers are used to create a wide range of products, from clothing and home textiles to industrial fabrics. Their versatility allows manufacturers to produce fabrics with varying textures, weights, and finishes, catering to the diverse needs of consumers. These fibers are particularly valued for their ability to enhance the softness and durability of fabrics, making them a popular choice for applications such as bedding, upholstery, and apparel. In the field of architecture, low melt polyester staple fibers are used in the production of nonwoven geotextiles and insulation materials. These materials provide essential functions such as soil stabilization, erosion control, and thermal insulation, contributing to the structural integrity and energy efficiency of buildings. The fibers' ability to bond with other materials at lower temperatures also allows for the creation of strong and durable composites, which are used in various construction applications. Beyond these primary sectors, low melt polyester staple fibers find use in a variety of other applications. For instance, they are used in the production of filtration materials, where their fine denier and ability to form strong bonds make them ideal for capturing particles and contaminants. They are also used in the production of hygiene products such as diapers and wipes, where their softness and absorbency are highly valued. As industries continue to seek materials that offer both performance and cost-effectiveness, the usage of low melt polyester staple fibers is expected to expand, driven by innovations and advancements in fiber technology.
Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market Outlook:
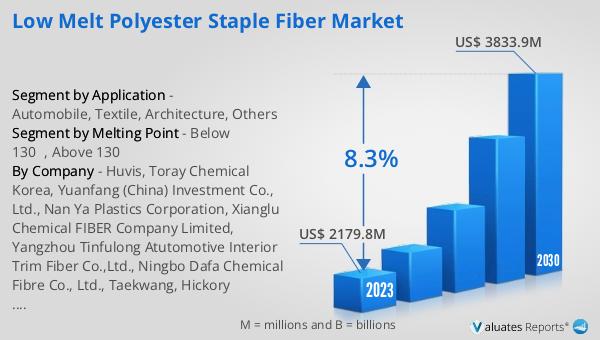
The outlook for the Global Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market indicates a promising growth trajectory. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately US$ 2621 million, and it is anticipated to expand significantly, reaching an estimated size of US$ 4717 million by 2031. This growth is expected to occur at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% over the forecast period. A notable aspect of this market is the concentration of production among the top three companies, which collectively hold a market share exceeding 40%. This indicates a competitive landscape where a few key players dominate the market. Geographically, China emerges as the largest production hub, accounting for more than 50% of the market share. This dominance is followed by South Korea, which holds a substantial share of approximately 35%. The significant production capacity in these regions underscores their importance in the global supply chain for low melt polyester staple fibers. The market's growth is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials across various industries, including automotive, textiles, and construction. As these industries continue to evolve and innovate, the demand for low melt polyester staple fibers is expected to rise, further fueling market expansion.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Low Melt Polyester Staple Fiber Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 2621 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 4717 million |
| CAGR | 8.5% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Huvis, Toray Chemical Korea, Yuanfang (China) Investment, Nan Ya Plastics Corporation, Xianglu Chemical FIBER Company, Yangzhou Tinfulong Atutomotive Interior Trim Fiber, Ningbo Dafa Chemical Fibre, Taekwang, Hickory Springs, Dividan, Sinopec Yizheng Chemical Fibre Limited Liability Company, CNV Corporation, Shyam Fibers, ECER, Anshun, by Melting Point, Below 130℃, Above 130℃ |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |