What is Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market?
Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market refers to a specialized segment within the animal nutrition industry that focuses on the use of chelated trace minerals in animal feed. Trace minerals are essential nutrients required in small amounts for the optimal growth, development, and overall health of animals. Chelation is a process that binds these minerals to organic molecules, enhancing their bioavailability and absorption in the animal's body. This market is driven by the increasing demand for high-quality animal products, such as meat, milk, and eggs, which necessitates the use of efficient and effective feed additives. Chelated trace minerals are preferred over inorganic minerals due to their superior absorption rates, reduced environmental impact, and ability to improve animal performance and productivity. The market encompasses various types of chelated minerals, including amino acids, proteinates, and polysaccharides, each offering unique benefits. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for sustainable and efficient animal nutrition solutions is expected to rise, further propelling the growth of the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market.
Amino Acids, Proteinates, Polysaccharides, Others in the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market:
Amino acids, proteinates, polysaccharides, and other compounds play a crucial role in the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market, each contributing to the enhanced bioavailability and efficacy of trace minerals in animal nutrition. Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as building blocks for proteins, and when used in chelation, they form stable complexes with trace minerals. This stability ensures that the minerals are protected from interactions with other dietary components, leading to improved absorption in the animal's digestive system. Amino acid chelates are particularly effective in enhancing the bioavailability of minerals like zinc, copper, and manganese, which are vital for various physiological functions, including enzyme activation, immune response, and bone development. Proteinates, on the other hand, are formed by binding trace minerals to short-chain peptides or proteins. This form of chelation not only improves mineral absorption but also provides additional nutritional benefits from the protein component. Proteinates are known for their ability to enhance the bioavailability of minerals such as iron, which is essential for oxygen transport and energy metabolism in animals. Polysaccharides, complex carbohydrates composed of sugar molecules, are another important component in the chelation process. When trace minerals are chelated with polysaccharides, they form stable complexes that are resistant to degradation in the digestive tract. This resistance ensures that a higher proportion of the minerals reach the site of absorption, leading to improved mineral uptake and utilization. Polysaccharide chelates are particularly beneficial for minerals like selenium, which plays a critical role in antioxidant defense and thyroid hormone metabolism. In addition to amino acids, proteinates, and polysaccharides, other compounds such as organic acids and hydrolyzed proteins are also used in the chelation process. These compounds offer unique advantages in terms of mineral stability and absorption, further enhancing the efficacy of chelated trace minerals in animal feed. The choice of chelating agent depends on various factors, including the specific mineral being supplemented, the target animal species, and the desired nutritional outcomes. Overall, the use of amino acids, proteinates, polysaccharides, and other compounds in the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market underscores the importance of optimizing mineral bioavailability to support animal health, productivity, and welfare. As the demand for high-quality animal products continues to rise, the role of these chelating agents in enhancing the efficacy of trace mineral supplementation is expected to become increasingly significant.
Ruminants, Swine, Poultry, Aquaculture in the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market:
The usage of Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market spans across various livestock sectors, including ruminants, swine, poultry, and aquaculture, each benefiting from the enhanced bioavailability and efficacy of chelated minerals. In ruminants, such as cattle and sheep, chelated trace minerals play a vital role in improving growth performance, reproductive efficiency, and overall health. Ruminants have a complex digestive system that can sometimes limit the absorption of inorganic minerals. Chelated minerals, with their superior absorption rates, ensure that essential nutrients like zinc, copper, and manganese are effectively utilized, supporting immune function, bone development, and milk production. In swine, chelated trace minerals contribute to improved growth rates, feed efficiency, and reproductive performance. Pigs have a relatively simple digestive system, and the use of chelated minerals ensures that essential nutrients are readily absorbed and utilized. This is particularly important during critical growth phases and reproductive cycles, where mineral deficiencies can lead to reduced performance and health issues. Chelated minerals also help in reducing the environmental impact of swine production by minimizing mineral excretion and improving nutrient utilization. In poultry, chelated trace minerals are essential for optimal growth, egg production, and overall health. Poultry species, such as chickens and turkeys, have high nutrient requirements due to their rapid growth rates and high productivity. Chelated minerals, with their enhanced bioavailability, ensure that essential nutrients like selenium, zinc, and copper are efficiently absorbed, supporting immune function, bone strength, and egg quality. The use of chelated minerals in poultry feed also helps in reducing the risk of mineral interactions and antagonisms, which can negatively impact nutrient absorption and utilization. In aquaculture, chelated trace minerals are crucial for supporting growth, health, and disease resistance in fish and shrimp. Aquatic species have unique nutritional requirements, and the use of chelated minerals ensures that essential nutrients are readily available for absorption. This is particularly important in intensive aquaculture systems, where mineral deficiencies can lead to reduced growth rates, poor feed conversion, and increased susceptibility to diseases. Chelated minerals also help in reducing the environmental impact of aquaculture by minimizing mineral excretion and improving nutrient utilization. Overall, the usage of Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market across ruminants, swine, poultry, and aquaculture highlights the importance of optimizing mineral bioavailability to support animal health, productivity, and welfare. As the demand for high-quality animal products continues to rise, the role of chelated minerals in enhancing the efficacy of trace mineral supplementation is expected to become increasingly significant.
Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market Outlook:
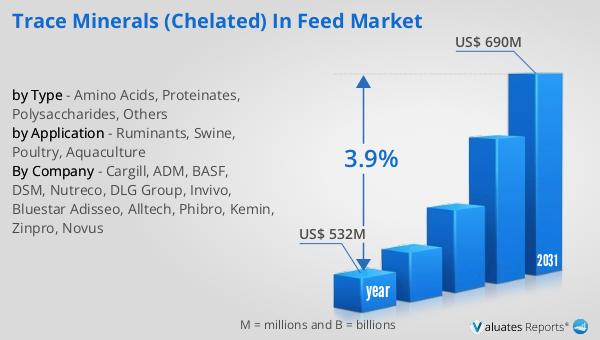
The global market for Trace Minerals Chelated in Feed was valued at $532 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow to a revised size of $690 million by 2031, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.9% over the forecast period. This growth trajectory underscores the increasing recognition of the benefits associated with chelated trace minerals in animal nutrition. As the demand for high-quality animal products continues to rise, driven by a growing global population and increasing consumer awareness of food quality and safety, the need for efficient and effective feed additives becomes paramount. Chelated trace minerals offer superior absorption rates compared to their inorganic counterparts, leading to improved animal performance, productivity, and overall health. This enhanced efficacy, coupled with the reduced environmental impact of chelated minerals, makes them an attractive option for livestock producers seeking sustainable and efficient nutrition solutions. The projected growth of the Global Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market reflects the ongoing advancements in animal nutrition science and the increasing emphasis on optimizing mineral bioavailability to support animal health and welfare. As the market continues to evolve, the role of chelated trace minerals in enhancing the efficacy of feed supplementation is expected to become increasingly significant, driving further innovation and development in this dynamic sector.
| Report Metric | Details |
| Report Name | Trace Minerals (Chelated) in Feed Market |
| Accounted market size in year | US$ 532 million |
| Forecasted market size in 2031 | US$ 690 million |
| CAGR | 3.9% |
| Base Year | year |
| Forecasted years | 2025 - 2031 |
| by Type |
|
| by Application |
|
| Production by Region |
|
| Consumption by Region |
|
| By Company | Cargill, ADM, BASF, DSM, Nutreco, DLG Group, Invivo, Bluestar Adisseo, Alltech, Phibro, Kemin, Zinpro, Novus |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |